📰 The supercomputer set to supercharge America’s AI future
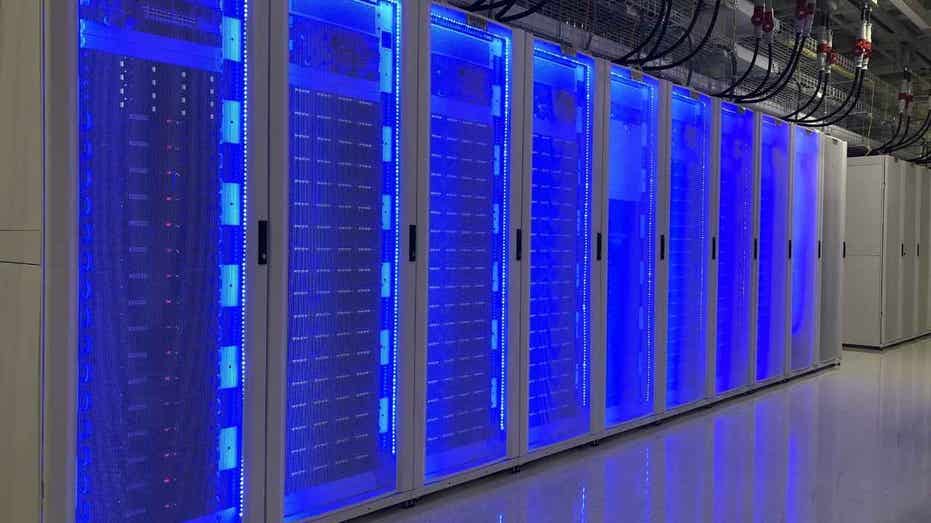

Georgia Tech is developing a supercomputer called Nexus with a $20 million investment from the NSF, expected to be operational in spring 2026. Nexus will offer over 400 petaflops of performance, specifically designed for AI research and high-performance computing tasks. The system features 330 terabytes of memory and 10 petabytes of flash storage, optimized for training large AI models and managing massive datasets efficiently. Nexus aims to balance power and ease of use, supporting various scientific workflows and enabling collaboration across different fields. The hybrid model of on-campus and national access ensures that Nexus drives innovation at all levels and contributes to real-world advancements in areas like healthcare, energy, and weather predictions.
📰 Bionic knee helps amputees walk naturally again
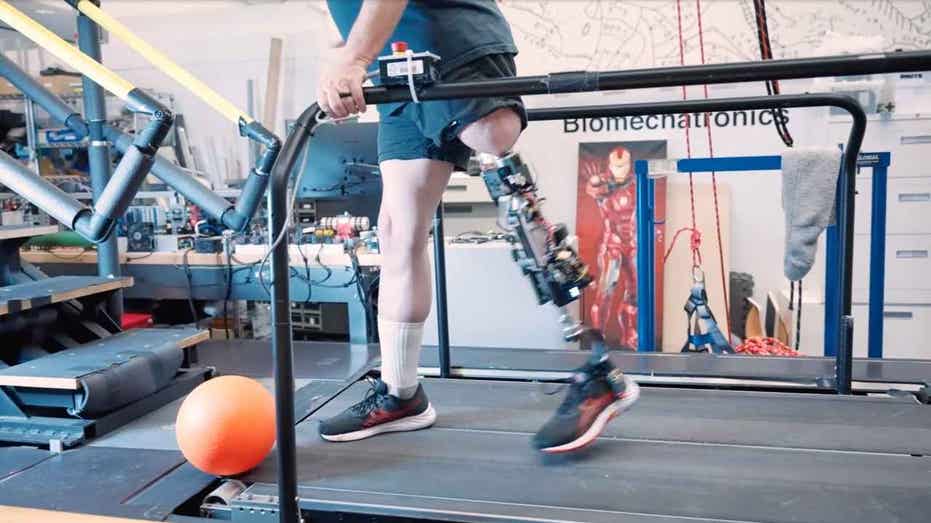
Researchers at MIT have developed a groundbreaking bionic knee that revolutionizes mobility for above-the-knee amputees. This innovative system directly anchors to the bone and integrates with muscle tissue, resulting in faster, smoother, and more natural movement. Led by Professor Hugh Herr, the MIT team’s solution goes beyond mimicking motion; it responds to the user’s intent, providing seamless and synchronized movement with the body. The technology, named e-OPRA, involves surgically implanting a titanium rod into the femur, creating a new interface between the body and a robotic prosthetic limb. Through specialized surgical techniques and muscle reconnection, patients experienced improved performance, comfort, and a sense of body ownership. While the e-OPRA system is not yet available on the market, larger clinical trials and FDA approval are on the horizon, potentially making this transformative technology more accessible within five years.
📰 This new air scanner could replace drug dogs at US borders
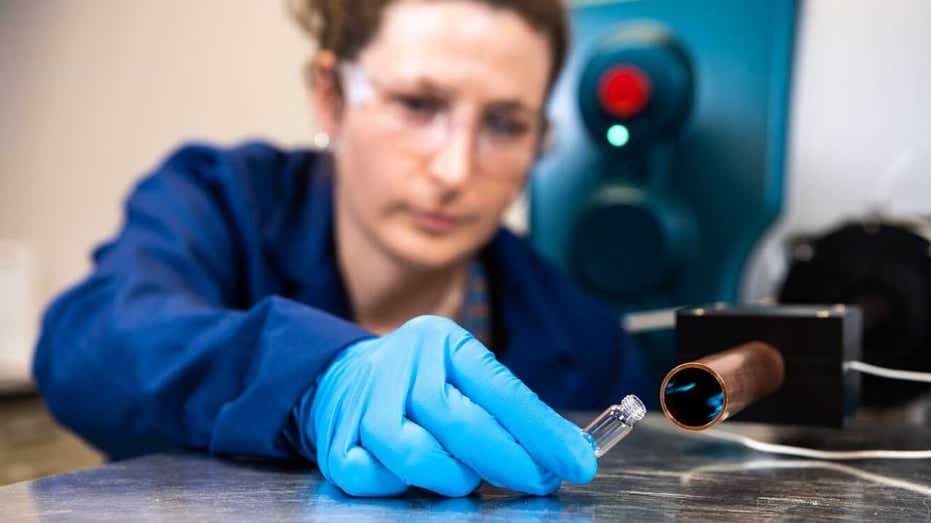

A new device called VaporID, developed by the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory and brought to market by BaySpec, is set to revolutionize border security by detecting drugs and explosives with unprecedented speed and accuracy. Unlike drug-sniffing dogs, VaporID can detect a wide range of substances, including fentanyl, cocaine, and explosives, in seconds. The device uses a miniature mass spectrometer to analyze molecules in real time, providing immediate results without the need for manual swab tests. VaporID’s sensitivity and efficiency make it a valuable tool for Customs and Border Protection in screening vehicles, cargo, luggage, and individuals at border crossings. The technology’s potential extends beyond borders, with plans to adapt it for mail screening, airport baggage checks, and large-scale cargo inspections to enhance national security efforts. As the U.S. faces a growing crisis of synthetic opioids, VaporID offers a contactless solution to intercept dangerous substances before they reach the streets, highlighting the evolving role of technology in border protection.
📰 How to hand off data privacy responsibilities for older adults to a trusted loved one

The article discusses the importance of protecting personal information, especially for older adults who are often targeted by scammers. It highlights the need for managing data privacy as fraud cases involving exposed personal data are on the rise. The article suggests involving a trusted loved one as a privacy partner to help navigate online security challenges. It emphasizes the significance of securing sensitive information like cell phone numbers, addresses, passwords, and accounts to prevent scams and fraud. The author provides practical tips on setting up security measures and seeking assistance from tech-savvy individuals while maintaining control over personal privacy.
📰 Humanoid robot performs medical procedures via remote control
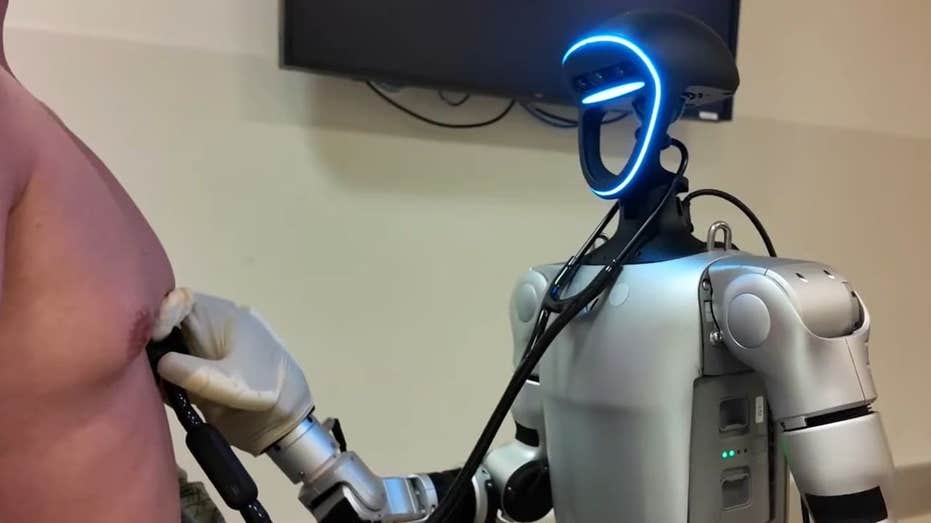

Healthcare systems globally face challenges like overcrowded hospitals, physician burnout, and surgery delays. The University of California San Diego (UCSD) is exploring the use of humanoid robots to alleviate these burdens. The Unitree G1 humanoid robot was equipped with Inspire Gen4 robotic hands and a bimanual teleoperation system to perform various medical procedures. The robot successfully carried out tasks like physical exams, emergency procedures, and ultrasound-guided injections, showing promise for training purposes. While the robot faced challenges with force control and sensor sensitivity, it demonstrated potential to support medical staff in routine and emergency care tasks. The research suggests that humanoid robots could enhance healthcare by providing faster, smarter care and relieving pressure on medical teams, especially in settings with labor shortages.
0개의 댓글